Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
1.
|
This is The FOA Online Design Self-Study Program Case Study
for FTTH.
This exercise covers the design of a FTTH Network.
This case study assumes
a leveel of understanding of fiber optics at the level of an FOA CFOT. THose not famillar with fiber
optics at that level may have difficluty with some of the exercises.
A large metropolitan
phone company has decided to test a FTTH network with the goal of deploying it throughout its system.
A typical link is shown below. Use common FTTH PON design parameters to design this
system.
Metro FTTH PON Link:
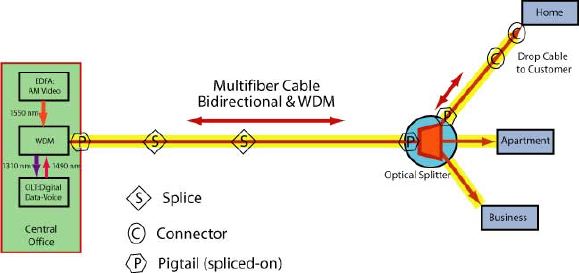
Basic System
Information:
| Segments | Length | Details | | CO/WDM to PON Coupler | 8 km | Multifiber SM cable, 2 intermediate splices, terminated with spliced-on pigtails on
both ends | | PON
Splitter to Drop | 500 m | Spliced
pigtail at PON, preterminated at drop end | | Drop to home | 100 m | Preterminated cable | | PON Splitter | | 32 port, 3
dB excess loss | | | | | | | |
| BPON
System | Transmitter
Wavelength | Transmitter Power
(dBm) | Receiver Power (Min) | Receiver Power (Max) | | Downstream Digital | 1490 nm | +3 dBm | -20 dBm | 0
dBm | | Downstream
AM Video (optional) | 1550 nm | +20
dBm | -5 dBm | 0 dBm | | Upstream Digital | 1310 nm | +3 dBm | -20 dBm | 0
dBm | | | | | |
Which PON option allows for both digital TV(IPTV) and analog video like
CATV?
|
Multiple
Choice
Identify the choice
that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
2.
|
The system will installed and initially operated as a BPON
system with triple play services..
What will be the wavelengths used for
transmission?
a. | 1310 nm | b. | 1490
nm | c. | 1550 nm | d. | 1310 and 1490
nm |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which one of the following fibers is the best choice for
this network?
a. | ITU G.652 - single-mode NDSF (non-dispersion-shifted
fiber) | b. | ITU G.653 - single-mode dispersion-shifted optical
fiber | c. | ITU G.654single-mode fiber which has the zero-dispersion
wavelength around 1300 m wavelength | d. | ITU G.655single-mode
NZ-DSF (nonzero dispersion-shifted) fiber), optimized for WDM and long-distance cable
runs |
|
|
|
4.
|
The cable for the 8 km link from the central office (C) to
the fiber distribution hub (FDH) which houses the PON splitter, will be pulled in available conduit.
The cable design chosen for that section of the link is a loose-tube design because the cable must be
_____.
a. | Water-blocked and armored | b. | Water-blocked and rated for high pulling tension | c. | Rated for aerial installation without a messenger | d. | UL Listed for flame retardance |
|
|
|
5.
|
The cable chosen for the section to the subscriber will be
aerial and therefore must be _____ .
a. | ADSS cable | b. | Figure-8 design
cable | c. | Loose tube cable lashed to a messenger or existing
cable | d. | Any of the above |
|
|
|
6.
|
How many fibers are required to connect each
home?
a. | One | b. | Two | c. | Four | d. | As many as
possible |
|
|
|
7.
|
In order to ensure the system will work on the cable plant
being designed, it is necessary to have what information on the communication system intended for use
on the cable plant?
a. | Wavelength | b. | Transmitter and receiver
power requirements | c. | PON splitter ratio and
excess loss | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
Typical Specifications
Provided for use as case
studies for design labs in FOA courses.
| Component
Specifications | | | | | Fiber
Loss | | | Singlemode
at 1310 nm | 0.4 dB/km (TIA 568: 1 dB/km) | | Singlemode at 1550 nm | 0.25 dB/km | | | | | Splice
Loss | (TIA 568: 0.3 dB, all types) | | Singlemode, fusion | 0.05 dB | | Singlemode, mechanical | 0.3 dB | | | | | Connector Loss | (TIA 568: 0.75 dB, all
types) | | Singlemode,
adhesive/polish | 0.3 dB | | |
Link margin specifications for most standardized fiber optic networks are on the
FOA Tech Topics Site (http://www.thefoa.org/tech/Linkspec.htm). It should be used as a reference for
designers and for the courses.
|
|
|
8.
|
Using the information supplied, the next step will be to
calculate the cable plant loss budget for this link.
For this GPON network,
____.
a. | Loss downstream will be less than loss
upstream | b. | Loss downstream will be more than loss
upstream | c. | Loss of the coupler is more downstream because it is a
splitter | d. | Loss of the coupler can be
ignored |
|
|
|
9.
|
Using the information supplied, calculate the cable plant
loss budget for this link.
Use the infomation in the "Typical Specifications" narrative
above.
a. | 21.90 dB | b. | 23.19
dB | c. | 21.90 dB downstream, 23.19 dB upstream | d. | 23.19 dB downstream, 21.90 dB upstream |
|
|
|
10.
|
For the equipment listed above, will the system operate on
this cable plant?
a. | Yes | b. | Yes, but may require an
attenuator at the transmitter end | c. | Yes, bmay require an
attenuator at the receiver end | d. | No, it cannot
work |
|
|
|
11.
|
What can be done on this system to get it to
work?
a. | Reduce the PON split to 16 subscribers | b. | Replace a connection with splices | c. | Use system equipment with
less margin | d. | Leave some PON splitter
ports unconnected |
|
Multiple
Response
Identify one or
more choices that best complete the statement or answer the question.
|
|
|
12.
|
What parameters should be tested and documented on this BPON
system cable plant to confirm proper installation?
|
|
|
13.
|
What should be included in the design documents to have the
customer prepare for restoration in case of an outage?
|